Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okamoto, Minoru; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
no journal, ,
In low-density nuclear matter which is relevant to the crust region of neutron stars and collapsing stage of supernovae, non-uniform structures called nuclear pasta are expected. Such pasta structures may play important roles, cooling process of neutron stars and the equation of state. So far, most works on nuclear pasta have used Wigner-Seitz cell approximation. We perform three-dimensional calculation of non-uniform nuclear matter based on the relativistic mean field model and the Thomas-Fermi approximation without any geometrical symmetry. Introducing a large cubic cell with periodic boundary conditions, we numerically solve the coupled field equations for mesons and the Coulomb potential. We demonstrate that the typical pasta structures appear in the three-dimensional calculations. The most stable structure and the EOS of matter with and without WS cell approximation are compared. Then we present newly observed structures which may appear as exited states of matter.
 C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction at TRIAC
O reaction at TRIACMakii, Hiroyuki; Miyatake, Hiroari*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Niki, Kazuaki*; Okada, Masashi*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Jeong, S. C.*; et al.
no journal, ,
The  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. Its reaction rate determines the mass fraction of
O reaction plays an important role in stellar evolution at the stage of helium-burning. Its reaction rate determines the mass fraction of  C and
C and  O, the abundance distribution of the elements between oxygen and iron, and the iron-core mass before the super-nova explosion. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of E2 cross section to E1 one. In order to provide a stringent constraint to extrapolation down to stellar temperature, additional data is crucial. Hence we designed new measurement at TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex). With use of the 18 GHz ECR (electron cyclotron resonance) ion source set upstream of the TRIAC accelerators, TRIAC has a possibility to deliver intense
O, the abundance distribution of the elements between oxygen and iron, and the iron-core mass before the super-nova explosion. However, the cross section at low energy still has a large uncertainty mainly due to the poor determination of the ratio of E2 cross section to E1 one. In order to provide a stringent constraint to extrapolation down to stellar temperature, additional data is crucial. Hence we designed new measurement at TRIAC (Tokai Radioactive Ion Accelerator Complex). With use of the 18 GHz ECR (electron cyclotron resonance) ion source set upstream of the TRIAC accelerators, TRIAC has a possibility to deliver intense  -beams. By using the pulsed alpha-beams provide by TRIAC, the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers, and enriched carbon targets (99.99 % enrichment in
-beams. By using the pulsed alpha-beams provide by TRIAC, the high efficiency anti-Compton NaI(Tl) spectrometers, and enriched carbon targets (99.99 % enrichment in  C), we measured the
C), we measured the  -ray spectrum of the
-ray spectrum of the  C(
C( ,
, )
) O reaction near the resonance at a center of mass energy of 2.4 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss obtained E1 and E2 cross sections of the reaction.
O reaction near the resonance at a center of mass energy of 2.4 MeV. In this contribution, we will discuss obtained E1 and E2 cross sections of the reaction.
Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Projectile charge-changing cross sections for nuclei in galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) on hydrogen play essentially important roles for the study of origin and source composition of GCRs. Previous experimental and theoretical works done so far made much progress on those cross sections. However, there are still uncertainties in much of the cross section data, and therefore the present knowledge of cross sections has not led to successful determination of the GCR source composition. To improve the uncertainties, a novel measurement system of projectile charge-changing cross section using CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors with excellent position and nuclear charge resolutions has been developed. We carried out measurements of total and partial charge-changing cross sections for Fe and Mg on 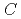 and
and 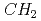 targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
Smith, M. S.*; Nesaraja, C. D.*; Lingerfelt, E. J.*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Kondev, F. G.*
no journal, ,
Nuclear masses are crucial in many areas of astrophysics, such as r-process nucleosynthesis in supernovae and rp-process nucleosynthesis in X-ray bursts. While there is significant effort internationally in new mass measurements and new theoretical mass models, the dissemination of mass information has not kept pace with these important developments. To address this problem, we have built an online, dedicated suite of codes - the nuclear mass toolkit at nuclearmasses.org. This free, platform-independent system enables scientists to quickly and efficiently share, manage, visualize, access, manipulate, compare, and analyze nuclear mass datasets. With our system, researchers can quickly and easily visualize them in customizable 1D and 2D plots, and calculate and plot RMS differences. We will demonstrate the utility of our site by comparing the RMS deviations of a wide variety of different theoretical mass models from experimental masses, over a variety of mass ranges.